What Is the Product of the Hydrogenation of an Alkene
Why is 2 Bromopropane the major product. The H ion is attracted to the πbond electrons of the alkene which forms a π complex.

Reduction Of Alkenes Hydrogenation Mcc Organic Chemistry
84 What is the product of the hydrogenation of an alkene.

. Addition of X 2 to Alkenes. What is the product of the hydrogenation of ethyne. Alkenes and alkynes are generally more reactive than alkanes due to the electron density available in their pi bonds.
Question What is the product of the hydrogenation of an alkene. This page looks at the reaction of the carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes with hydrogen in the presence of a metal catalyst. And youll see other definitions for oxidation states.
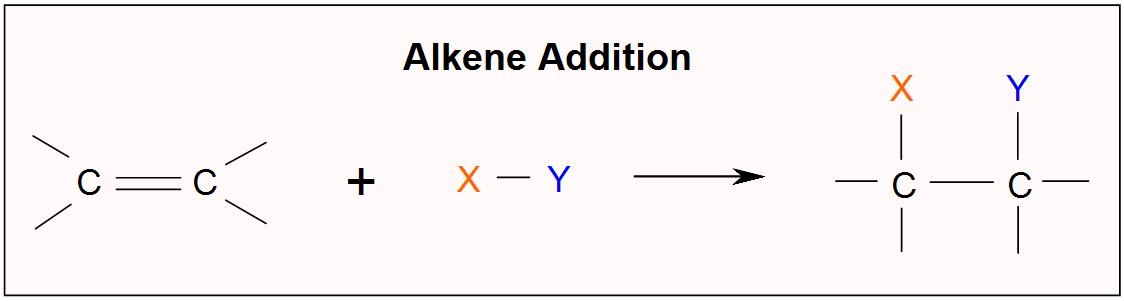
Ethylene ethene 2 H 2 CCH 2 is an alkene an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Chemistry questions and answers. An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenationIn a hydrogenation reaction two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene resulting in a saturated alkane.
An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenationIn a hydrogenation reaction two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene resulting in a saturated alkane. Alkyne hydrogenation adds hydrogen atoms to the pi bond s. What is the product of the hydrogenation of an alkene.
The product is an alkane. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. What does alkene hydrogenation explain.
The only product involved in the hydrogenation of alkenes is the resulting alkane. The heat released is called the heat of hydrogenation which is an indicator of a molecules stability. Hence we can say that ethane is the product of the hydrogenation of ethyne.
The product is an alkane. 84 What the product of the hydrogenation of an alkene. Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. To sway the equilibrium one way or another the temperature or the concentration of the non-nucleophilic strong acid can be changed. It includes the manufacture of margarine from animal or vegetable fats and oils.
What is the product formed from hydrogenation reaction of ethene. Examples of Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes. Since a large heat of reaction indicates a high energy.
So the alkene is reduced by the addition of these two hydrogens. The first step in the addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene is the dissociation of the hydrogen halide. This heat of reaction can be used to evaluate the thermodynamic stability of alkenes having different numbers of alkyl substituents on the double bond.
We call this reaction as hydrogenation of alkenes. Ethane It forms ethane ie. The hydrogenation of ethene Ethene reacts with hydrogen in the presence of a finely divided nickel catalyst at a temperature of about 150C.
Halogenation and hydrogenation are examples of the addition of X 2-type molecules to alkenes. The π complex then breaks creating a σ single bond between one carbon of the doublebonded pair and the hydrogen. Youll see a gain in hydrogens is reduction.
Who are the experts. This process yields semi-solid products like shortening and margarine. For example the following table lists the heats of hydrogenation for three C 5 H 10 alkenes which give the same alkane product 2-methylbutane.
However the mechanisms are completely different as shown by the stereochemistry of the addition products. Electrophilic hydration is reversible because an alkene in water is in equilibrium with the alcohol product. Hydrogenation of a double bond is a thermodynamically favorable reaction because it forms a more stable lower energy product.
If only one pi bond is replaced with carbon-hydrogen. Hydrogenation of alkenes is a reduction process wherein the addition of molecular hydrogen breaks. If both pi bonds are replaced with carbon-hydrogen bonds then an alkane forms.
The catalyst is reformed so the reaction starts and ends with the same catalyst. Alkenes are reduced to alkanes in the hydrogenation. It will undergo catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of a nickel catalyst Ni.
This means that when hydrogen is added to carbon-1 which has more hydrogen and bromine is added to carbon-2 the product 2-bromopropane will be the major product. Alkene reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of catalyst to give alkane as the product. The product of this reaction is ethane CH.
Hydrogenation is used in the food industry to convert liquid oils into saturated fats. This is called hydrogenation. 85 Provide the structure of the major organic product in the reaction below.
An example of an alkene addition reaction is a process called hydrogenationIn a hydrogenation reaction two hydrogen atoms are added across the double bond of an alkene resulting in a saturated alkane. In this manner what is the product of the hydrogenation of an alkene. Hydrogenation is used in the food industry to convert liquid oils into saturated fats.
Heres a video on the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. This process yields semi-solid products like shortening and margarine. Hence according to Markovnikov Rule when hydrogen is added to the carbon with more hydrogen we will get the major product.
See the answer See the answer done loading. Name one catalyst used in this reaction. One might assume that the reaction mechanism of the addition of halogens to alkenes is very similar to that of the addition of hydrogen.
Heres a video on the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. Hydrogenation of a double bond is a thermodynamically favorable reaction because it forms a more stable lower energy product. Alkane O dihaloalkane O ether O alcohol O haloalkane.
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=409&height=109)
Catalytic Hydrogenation Of Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
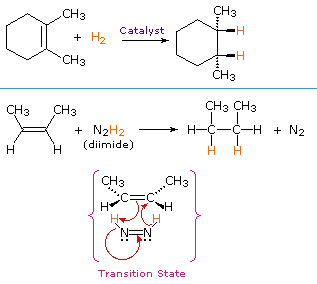
Hydrogenation Of Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts

Comments
Post a Comment